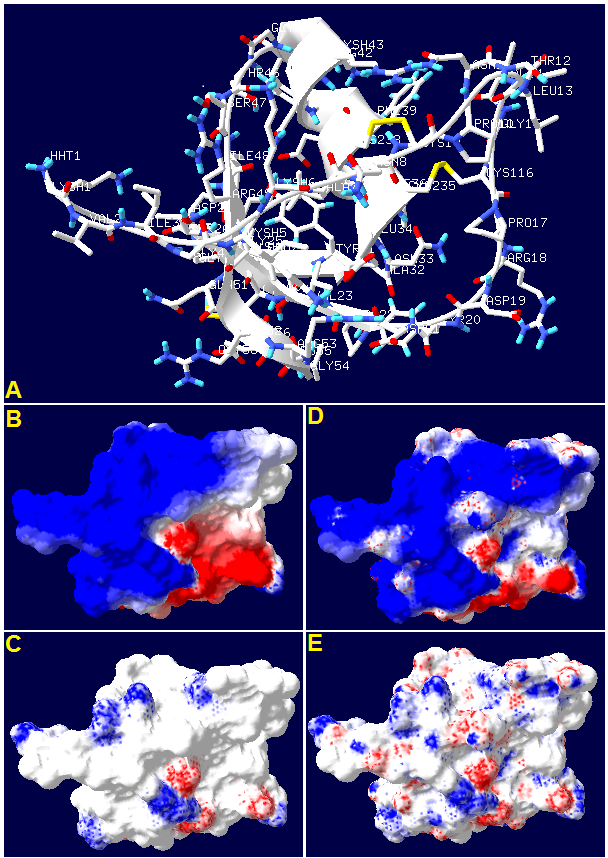
Structural prediction and in silico physicochemical characterization for mouse caltrin I, rat caltrin and bovine caltrin proteins. Recognition events and interactions between rat caltrin and model membranes.
Dr. Ernesto J. Grasso
It is known that caltrin (calcium transport inhibitor) protein binds to sperm cells during ejaculation and inhibits the extracellular Ca2+ uptake. Although the sequence and some biological features of mouse caltrin I, rat caltrin and bovine caltrin are known, their physicochemical properties and 3D structures are mainly unknown. We predicted the mouse caltrin I, rat caltrin and bovine caltrin 3D structures by molecular homology modeling and threading. Surface electrostatic potentials and electric fields were calculated using the Poisson-Boltzmann equation. Several different bioinformatic tools and available web servers were used to deeply analyze the physicochemical characteristics of both proteins, such as Kyte and Doolittle Hydropathy score and helical wheel projections. Equilibrium spreading pressure was obtained by Gibbs adsorption isotherms. Interactions between rat caltrin and phospholipids model membranes were defined by penetration (cut off) studies. We observed that rat caltrin is able to penetrate directly to membranes, but mainly in negatively charged surfaces and expanded lateral phase states. The results presented in this work have significant relevance to further understanding the molecular mechanisms of caltrin proteins to modulate physiological processes associated with fertilization